What Is Air Pollution? Causes Of Air Pollution
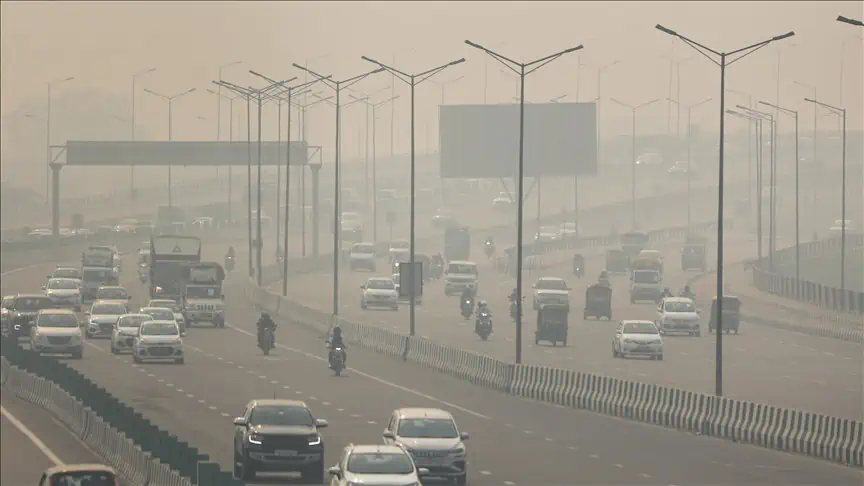

What Is Air Pollution?
Air pollution refers to contaminated indoor or outdoor air. Pollution can be any atmospheric air alternations, whether physical, biological or chemical. Whenever contaminants like dust or smoke enter the atmosphere, vegetation, humans and other living beings may have trouble surviving. Air pollution also refers to a substance that hinders the atmosphere and ecosystem.
The composition of gases in the atmosphere sustains all living things on Earth, and any imbalance may cause harm to life.
Air Pollutants
Air pollutants are classified into two types:
Primary pollutants are those that contribute directly to air pollution. Sulfur dioxide, emitted by factories, is a primary pollutant.
Secondary Pollutants
Secondary pollutants are those that are formed as a result of primary pollutants mixing and reacting. Smog is a secondary pollutant produced by the combination of smoke and fog.
The Most Common Causes of Air Pollution?
Air pollution is caused by both naturally occurring and manmade pollution sources, both of which may harm human health. Natural sources include volcanic eruptions, dust carried by the wind and gases released by living beings. Manmade activities that cause air pollution include motor vehicle use, fossil fuel burning and agriculture.
The most common air pollution sources include:
1. The Use Of Fossil Fuels
Most air pollution is caused by the combustion of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gasoline to generate energy for electricity or transportation. The amount of carbon monoxide released indicates how much fossil fuel is burned.
As a result, other toxic pollutants are released into the atmosphere. Inhaling polluted air from natural gas and fossil fuel combustion reduces the heart’s ability to pump enough oxygen, resulting in respiratory illness.

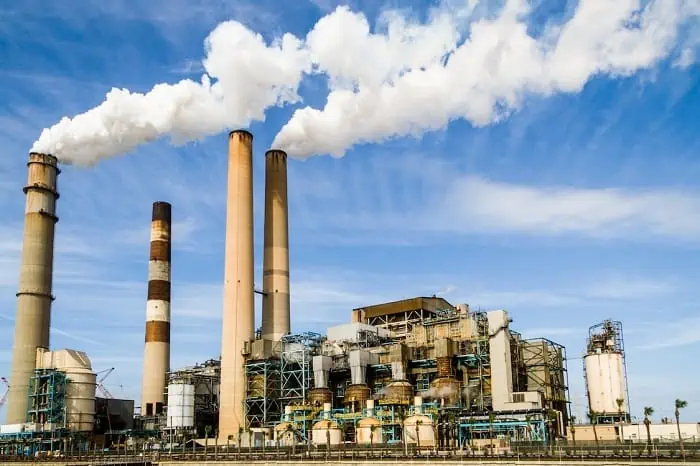
2. Emissions From Industry
This is one of the major causes of air pollution. Industrial activities emit various pollutants into the atmosphere, which have far-reaching consequences for air quality.
Particulate matter 2.5 and 10, nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and carbon monoxide are significant pollutants emitted by industries that use coal and wood as their primary energy source for manufacturing goods.
The effects of industrial pollution on your health can range from irritation in your eyes and throat to breathing problems and can even lead to chronic illness.

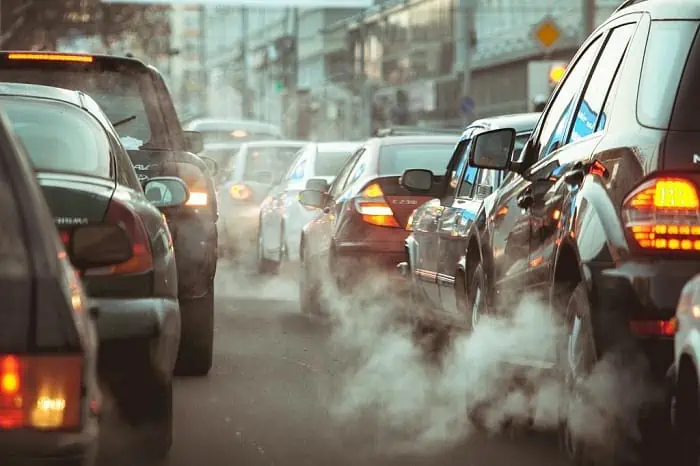
3. Transportation
There is no denying that vehicle pollution is a major source of air pollution, particularly in cities. When a car burns gasoline, it emits pollutants into the atmosphere that are as harmful as smoking ten cigarettes per day.
Carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, nitrogen oxide, and particulate matter are emitted by vehicles. When there is a high level of vehicle pollution in the atmosphere, it causes a hole in the ozone layer, which contributes to smog and causes various health problems.

4. Agriculture-related Activities
Ammonia is one of the most dangerous gases in the atmosphere and is a common byproduct of agricultural activities. In agricultural activities, the use of insecticides, pesticides, and fertilizers has increased significantly.
They release harmful chemicals into the atmosphere and can pollute the water. Farmers also burn the fields and old crops to keep them clean for the next round of sowing. The burning of fields also causes air pollution by releasing harmful gases.

5. Building And Demolition
The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) received the most air pollution complaints in the Delhi NCR during the clean air act movement, owing to construction pollution and demolition activities.
Construction and demolition are an ongoing part of the national capital’s development phase as the city’s population grows. Several construction sites and raw materials, such as bricks and concrete, produce haze and foul air, endangering children and the elderly.

6. Process Of Microbial Decay
Carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, chemicals, and organic compounds are all released by the manufacturing, chemical, and textile industries, contaminating our environment.
Bacteria and fungi play critical roles in nature’s biogeochemical cycles, and they are the essential indicators of abnormal environmental conditions. T
The decay of these microorganisms in the environment produces methane gas, which is highly toxic, and breathing toxic gases such as methane can be fatal.
7. Landfills And Waste
Landfills are plots of land where waste is dumped or buried, and methane is produced when waste is deposited or buried. Methane is a major greenhouse gas that is highly flammable and dangerous.
Another major issue is e-waste, which involves a variety of unscientific dismantlers, such as chemical leaching, burning wires, and others.

8. Exploration And Mining
Mining is the extraction of minerals from the earth’s crust using heavy machinery. Dust and chemicals are released into the air during the process, causing massive air pollution. This is one of the factors contributing to the deterioration of workers and nearby residents’ health.

9. Eruptions Of Volcanoes
Some people believe that air pollution is entirely man-made. That is not 100% true. Natural processes emit a large number of pollutants into the atmosphere which causes air pollution.
According to National Geographic, sulfur dioxide is a major modern air pollutant, and volcanoes can emit enough sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere to influence global cooling.

10. Forest Fires
Forest fires emit pollutants into the atmosphere in the same way that fireplaces burning wood do. They emit fine smoke particles that, according to the EPA, are small enough to enter the lungs and cause damage to the lungs and heart.

11. Activities in the Home
Forget about pollution in the environment. What about the pollution that occurs within our own homes? The following are some everyday household items that can contribute to indoor air pollution: