Types Of Dams & Their Uses

What Is Dam?
A dam is a hydraulic structure built across a river or a stream to create a reservoir for the available water. A dam is also referred to as a barrier which is built across a river or a stream to restrict and control the flow of water.
Dams may be built as small as an embankment dam, built to provide adequate quantity of water in farms, or as large as a massive concrete structure, for various purposes.
The reservoir created by dams provides water for various purposes such as human consumption, agriculture activities, industrial use, hydropower generation, etc.
Types Of Dams
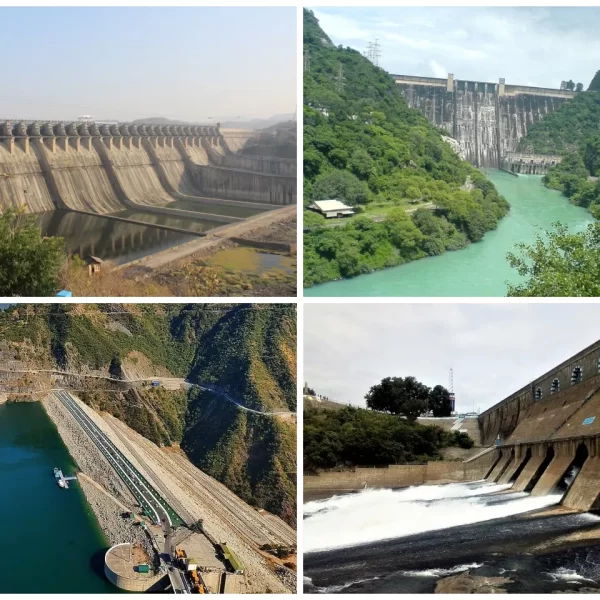

There are various types of dams which are constructed for different purposes. All of these dams are classified according to their use, hydraulic design, material, and structure, and design. Let us learn about each type of dam in detail below.
Classification Of Dams Based On Use
- Storage Dam
- Diversion Dam
- Detention Dam
- Debris Dam
- Cofferdam
Classification Of Dam According To Hydraulic Design
- Overflow Dam
- Non-overflow Dam
Classification Of Dams Based On Materials
- Masonry Dam
- Concrete Dam
- Timber Dam
- Steel Dam
- Earth Dam
- Rockfill Dam
Classification Of Dams According To Structure & Design
- Gravity Dam
- Arch Dam
- Buttress Dam
Classification Of Dams Based On Use
1. Storage Dam
Storage dams are constructed to store water during the monsoon season when the water is available in excess amount and the flow of water in the river is considerably good.
The water stored in the dam is utilized for various activities like human utilization, agriculture, hydropower generation, etc. If not specified, in general terms, dam means storage dam only.
2. Diversion Dam
Diversion dams are mainly constructed to divert water to the river. The storage capacity of the diversion dam is lesser. Diversion dams are usually of lower heights. Weirs and barrages are examples of diversion dams.

3. Detention Dam
Detention dams are constructed for flood control. The detention dam slows down the flow of flood water in the river on its downstream.
It also stores some of the flood water to slow down the flow and then releases the water gradually at a controlled rate for its required use. Detention dams protect the downstream area from floods.
4. Debris Dam
The river water sometimes contains impurities of small and big sizes such as wood planks, plant waste, sand, gravel, etc. So the major purpose of a debris dam is to retain such substances in rivers.
When the water passes through a debris dam in a river, the dam retains the debris and only allows the water to pass through it. The water when passes through it are clear and free from such harmful substances.
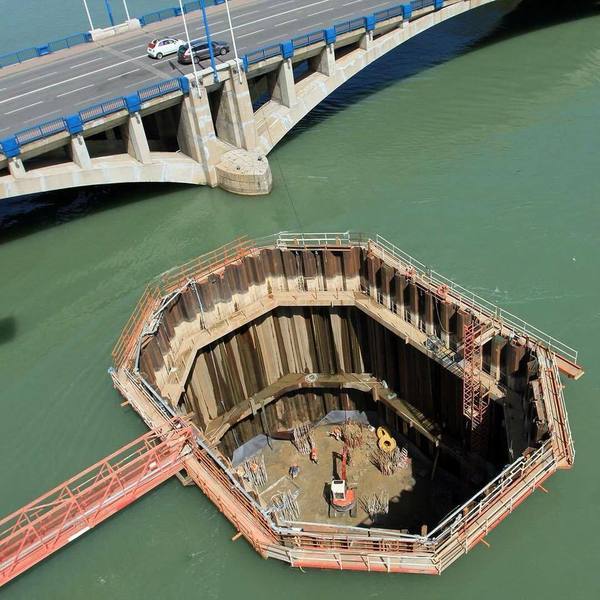
5. Cofferdam
A cofferdam is a temporary structure constructed to allow construction activities to take place in rivers or any other water body. A cofferdam is constructed to provide a dry area so the construction activities can easily take place.
After the cofferdam is constructed, the water from it is pumped out to make it a dry area. Cofferdams are usually constructed on the upstream side of the river.

Classification Of Dam According To Hydraulic Design
1. Overflow Dam
It is a type of dam that permits the water to flow over its crest when excess water flows on the upstream side of a river. Overflow dam is designed in such a way that the crest level is usually constructed at a lower height relatively, to allow the surplus water to overflow. Overflow dams are generally made up of concrete or masonry. Overflow dam is also known as spillway or overfall dam.
2. Non-overflow Dam
Unlike overflow dams, the structure of a non-overflow dam is designed and constructed in such a way that the water is not allowed to overtop the dam. The height of the dam is usually kept higher than the maximum expected High Flood Level (HFL).
Classification Of Dams Based On Materials
1. Masonry Dam
These dams are constructed out of materials like stone and bricks. Cement mortar is used for bonding blocks of stone masonry. Examples of such dams are gravity dams and arch dams.
Nagarjunasagar Dam is the largest masonry dam in the world. It is situated in Andhra Pradesh, India. The height of the Nagarjunasagar dam is 125m.

2. Concrete Dam
Concrete is widely used to construct not only dams but, different types of structures all over the world. Concrete is a rigid material when matures properly. So these dams are also known as rigid dams.
Concrete dams are highly durable and are designed to carry and withstand heavy loads and pressure. The majority of dams in the world are built using concrete. Examples of concrete dams are gravity dams, arch dams, and buttress dams.

3. Timber Dam
Timber dam is a temporary structure constructed to divert water for a temporary period so the construction of the main dam can take place. The structural members or the load-bearing members of this dam are mainly built up using wood like pine wood and fir wood.
Timber dams are also used to control the floodwater during the rainy season. These types of dams are suitable for a height of up to 8 to 10 meters.

4. Steel Dam
Steel dams are also used as temporary structures like timber dams. Steel dams are more durable and stronger than timber dams. The purpose of steel dam is similar to the timber dams. Steel dams are suitable for a height of up to 15 meters. Steel dams are also under the category of rigid dams.

5. Earth Dam
Earth dams are the most common types of dams. They are built using the locally available soils and gravels. It is a type of non-rigid dam.
Earth dams are suitable for moderate heights as the material used for the construction of earth dams may not be feasible for greater heights.
The construction procedure of an earth dam is less complex than other types of dams. Earth dams are a type of embankment dam.

6. Rockfill Dam
Like the earth dams, Rock fill dams are embankment type dams, also categorized as non-rigid dams. Rocks of various sizes are used in the construction of rockfill dams, which provide stability to the structure.
Rockfill dams are also consisted of an impermeable membrane to provide water tightness. Rockfill dams are comparatively cheaper in terms of cost as compared to other types of dams.

Classification Of Dams According To Structure & Design
1. Gravity Dam
Gravity dams are the type of dams in which the external forces coming on it such as the pressure of water, the pressure of waves, and the uplift pressure, are resisted by the weight of the dam itself.
The stability of gravity dam fully depends on its weight. Gravity dams were primarily constructed out of masonry components such as stones or bricks. But nowadays, these dams are constructed using concrete.
Gravity dams are stronger and more durable as compared to earth dams. Also, the height of the gravity dam is more due to its construction using concrete, as concrete is a rigid material. The initial cost of constructing a gravity dam is higher, but it may prove to be a cheaper option in the long run.

2. Arch Dam
An arch dam is curved in plan. It has convexity towards the upstream side of the dam. An arch dam transfers all the external forces coming on it to the abutments by its arch action.
An arch dam is usually constructed where the width of the river or stream is narrow with strong banks to withstand various forces. The section of an arch dam is thinner than a gravity dam.

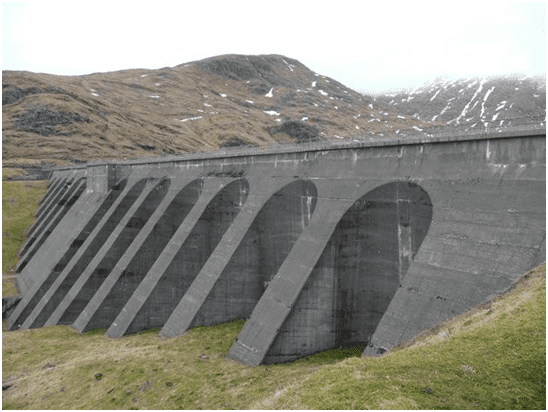
3. Buttress Dam
A buttress dam consists of a buttress, face slab, and base slab components. The face slab is situated on the upstream side. Buttresses are provided at certain intervals behind the face slab. The face slab is somewhat in an inclined position.
Buttresses are provided as support elements in the buttress dam. Buttress dams may be straight or curved in plan. Buttress dams are usually built where the soil is comparatively weaker. Buttress dams are made using concrete.